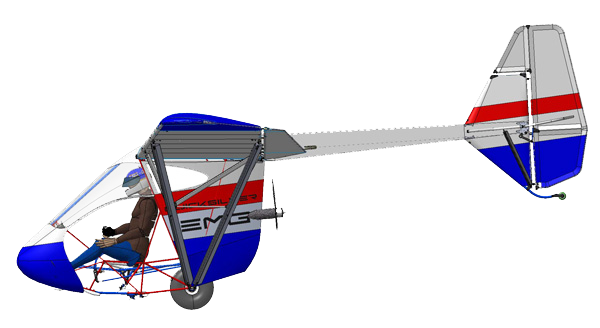
MGM Compro is a Czech company that seems to have a motor on half of every light electric airplane flying today. Their motors have powered Airbus’s electric Cri-Cri (four 15-kilowatt units), the firm’s e-Fan, Ruppert Composite’s Archaeopteryx, e-Volo’s Volocopter, and any number of motorgliders and light sport aircraft buzzing quietly over Europe, and soon, America. Certification in Europe Certification is usually the route to wide acceptance of a new motor, proof that the unit has passed some rigorous tests and is suited for use in aircraft. As Martin Dvorsky, Managing Director for the firm reports: We are really proud to announce that [the] MGM COMPRO complex propulsion unit just obtained [a] CERTIFICATE OF AIRWORTHINESS issued by [the] Slovak Federation of Ultra Light Aircraft. This certificate means that the glider and its system has positively passed all the safety and flight tests and can be legally operated by LSZ license holder (UL license counterpart).” Note the clever motor and propeller folding and retraction …
A 24-Volt Airplane Motor?
One of the big surprises in last month’s webinar hosted by the EAA and presented by Brian Carpenter of Rainbow Aviation Services/Adventure Aviation was the 24-Volt motor being developed for the EMG-6 ultralight motorglider. High and Low Voltages Many, if not most of the electric motors flying on existing craft are higher voltage units. For sake of an off-handed definition, we’ll divide low and high at below and above 50 Volts, something OSHA delineates in its regulation 29 CFR 1910.303(g)(2)(i), which “generally requires “’live parts of electric equipment operating at 50 volts or more’ to be ‘guarded against accidental contact by use of approved cabinets or other forms of approved enclosures’ or by other specified means.” In its explanation, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration “considers all voltages of 50 volts or above to be hazardous. Electric current, not voltage, passing through the human body causes injury….” And it really doesn’t take much amperage to take a person to the …