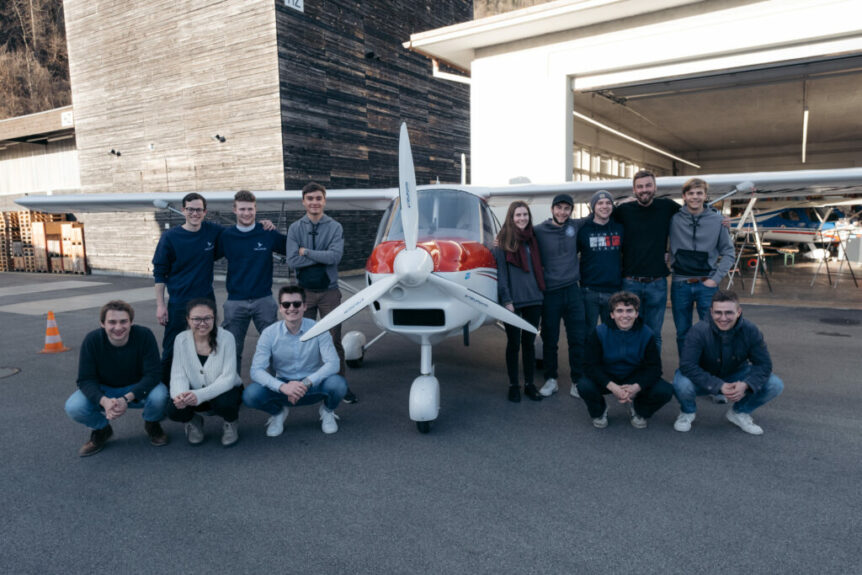
The Cellsius AC4 Lightwing is a capable microlight aircraft popular in Europe. As part of a project to clean up aviation, it will fly on hydrogen, and for good distances if students at ETH Zurich* are successful in their project. Students are modifying a Lightwing to run on pressurized H2, and crafting motor, fuel system, tanks, power electronics, and battery backup system to make a coordinated, custom-fitted craft. It will stay aloft for two hours and emit nothing but water vapor. The project’s web site spells out the students’ ambitions. “Our powertrain consists of many components that together can get an aircraft into the air. “To make this a reality, we develop the majority of our components ourselves, tailored to our requirements.” Components include a radial-flux motor, unusual in that most electric aircraft motors are axial flux. Students worked with e+a (Elektromaschinen und Antriebe) AG to design and construct the unit. With that motor, students helped design a matching inverter …
Recycling and Reusing Carbon in Jet Fuel
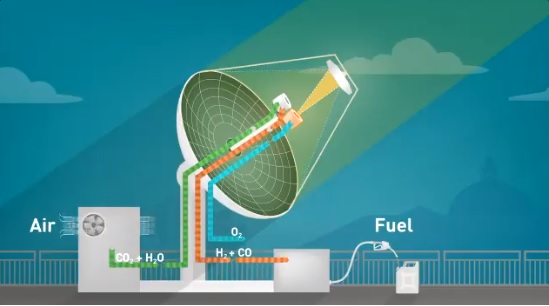
ETH Zurich (the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology), is recycling and reusing CO2 to make jet fuel as part of a carbon-neutral process. This is not a new idea, with others’ approaches to this detailed in earlier blog entries here, here, and here. Centered on a solar collector/reactor on the roof of ETH’s Machine Laboratory building in Zurich, researchers have “developed a novel technology that produces liquid hydrocarbon fuels exclusively from sunlight and air and have demonstrated the entire thermochemical process chain under real field conditions.” Extracting CO2 and water directly from ambient air through an adsorption/desorpton process, the system feeds these free materials into a solar reactor that is at the focus of the parabolic reflector that heats them to 1,500° Celsius. A cerium oxide structure in the reactor enables a redox (oxidation-reduction reaction)* cycle, with syngas an end product. This gas can be processed into a commercially-viable hydrocarbon fuel through conventional methanol or Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, according to GreenCarCongress. …
Earth, Air, Water and Jet Fire
“I have always loved the desert. One sits down on a desert sand dune, sees nothing, hears nothing. Yet through the silence something throbs, and gleams.” Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, The Little Prince The SOLAR-JET project (Solar chemical reactor demonstration and Optimization for Long-term Availability of Renewable JET fuel. or SOLAR-JET) pulls carbon dioxide from the air, mixes it with water and exposes the mix to 1,500 degree (Centigrade) concentrated solar energy and makes a synthetic natural gas, with oxygen as the only exhaust. Attempting to produce a useable fuel from CO2 has been an obsession for many over several decades. Attempts to capture and store CO2 are expensive and usually only hide the carbon, ostensibly for eternity. SOLAR-JET explains its objectives on its web site. “The aim of the SOLAR-JET project is to demonstrate a carbon-neutral path for producing aviation fuel, compatible with current infrastructure, in an economically viable way. Because the process hopes to pull CO2 from the atmosphere, the …
UAVs Push Endurance Limits
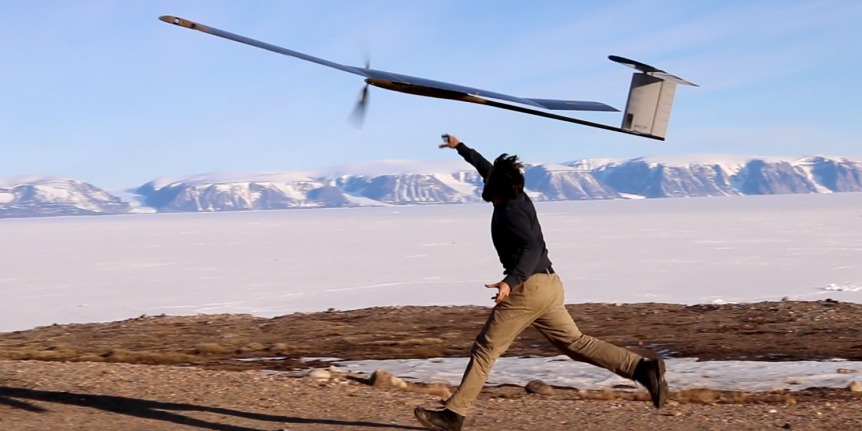
Three unpiloted aerial vehicles of wildly different configurations recently set endurance marks, each a “personal best,” with some achieving world records. The varying designs show what can be achieved by careful aerodynamic design and efficient powerplants. Aerovel Flexrotor Sets VTOL Endurance Mark Not just a fair weather UAV, Aerovel’s unmanned Flexrotor, named for the sea nymph Actaea, “lifted off into a grey and rainy morning with 7.5 kilograms (16.5 pounds) of fuel onboard”. According to the company, “It transitioned from hover to wing-borne flight, and soldiered on through a showery day, a blustery night, and then another day in the breezy and unsettled air behind a cold front. As dusk fell it transitioned back to hover, and dropped gently down onto a 12-foot square helideck underway at 8 [knots] (9.2 mph). Time from launch had been 32 hours and 8 minutes. More than 3 hours’ worth of gasoline remained in the tank.” The press release doesn’t say where the flight took …