Lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries face several problems: they are not making great leaps forward that we hope for, they occasionally burst into flame, and they weigh too much to be all that practical in a pure-electric airplane. Researchers peer over the alternatives, magnesium, manganese, aluminum, and now, after several false starts in recent years, zinc. University of Sydney scientists claim to have found a three-stage method of charging zinc-air cells that promises greater energy density and longevity. One selling point – the relative abundance and low cost of zinc, such cells are cheaper to produce than lithium equivalents. They theoretically can store up to five times more energy than lithium-ion cells, are less prone to burst into flame, and are even more environmentally friendly. What’s not to like? Until now, they’ve been difficult to recharge. ReVolt tried developing a rechargeable zinc-air battery with an ARPA-E (Advanced Research Projects Agency – Energy) grant, but gave up after two years. Explaining that …
Cheap Hydrogen, Anyone?
Researchers in Glasgow and at Stanford University have devised ways to decouple oxygen and hydrogen from water without resort to expensive extraction or storage techniques. Both breakthroughs involve low-cost materials, low-energy requirements, and the production of clean hydrogen through what should be renewable energy resources. The latter overcomes one major objection to hydrogen production. As Professor Lee Cronin of the University of Glasgow’s School of Chemistry explains, “Around 95% of the world’s hydrogen supply is currently obtained from fossil fuels, a finite resource which we know harms the environment and speeds climate change. Some of this hydrogen is used to make ammonia fertilizer and as such, fossil hydrogen helps feed more than half of the world’s population. “The potential for reliable hydrogen production from renewable sources is huge. The sun, for example, provides more energy in a single hour of sunlight than the entire world’s population uses in a year. If we can tap and store even a fraction of …
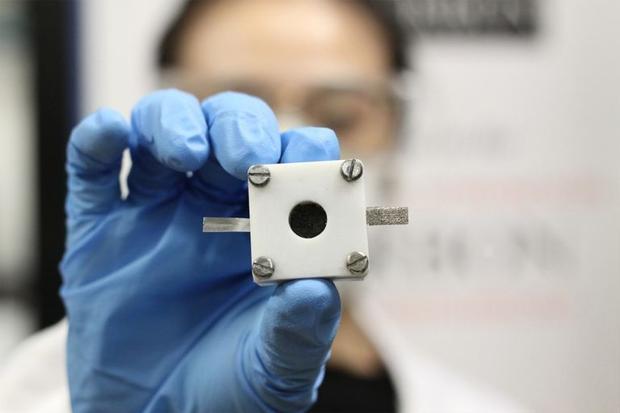
Stanford scientists develop high-efficiency zinc-air battery
Battery researchers, including those at Stanford University, have been focusing for years on improving lithium batteries of multiple chemistries. While IBM tries to create the 500-mile battery based on lithium-air reactions, and ReVolt in Portland works on perfecting a long-lasting zinc-air cell, Stanford researcher Hongjie Dai and his team claim to have “developed an advanced zinc-air battery with higher catalytic activity and durability than similar batteries made with costly platinum and iridium catalysts.” The resulting battery, detailed in the May 7 online edition of the journal Nature Communications, could be the forerunner of something with greater endurance and lower cost than current efforts. Mark Schwartz, writing for Stanford, quotes Dai, a professor of chemistry at the University and lead author of the study: “There have been increasing demands for high-performance, inexpensive and safe batteries for portable electronics, electric vehicles and other energy storage applications. Metal-air batteries offer a possible low-cost solution.” Lithium-ion batteries, despite their limited energy density (energy stored per …
Thomas Alva Would Be Proud
The best batteries as now produced use expensive materials and processes to achieve high energy density. Could a century-old idea be resurrected to provide an inexpensive alternative to today’s costly electric storage devices? Science Daily reports on a recent attempt to improve on a proven technology. Stanford University’s Hongjie Dai, professor of chemistry and head of a research group, is working with the Edison battery, named for Thomas Alva Edison, and using the nickel-iron electrodes Edison favored, but with a modern twist to overcome one of its disadvantages. Stanford’s news bulletin quotes Dai. “The Edison battery is very durable, but it has a number of drawbacks. A typical battery can take hours to charge, and the rate of discharge is also very slow.” Powering electric vehicles in the early 1900s, Edison’s battery is used today in limited instances to store surplus electricity from solar panels and wind turbines where charging and discharge speeds are not a major consideration. Dai’s …
Imperfect Carbon as Good as Pricy Platinum
The expense of platinum catalysts has been an impediment to the development of fuel cells and metal-air batteries. Scientists at Stanford University may have found an inexpensive, higher-performance alternative in “unzipped” carbon nanotubes that show an imperfect face to the world. Findings published in the May 27 online version of the journal Nature Nanotechnology quote chemistry professor Hongjie Dai, co-author of the paper. “Platinum is very expensive and thus impractical for large-scale commercialization. Developing a low-cost alternative has been a major research goal for several decades.” With platinum ranging from almost $800 to over $2,200 an ounce, carbon nanotubes, with their conductivity and inexpensive production costs provide a desirable combination of performance and price. Nanotubes are rolled-up sheets of graphene, a one-atom thick layer of pure carbon – 10,000 times narrower than a human hair. Dai’s team nested two or three nanotubes, each smaller than the next layer outward, an amazing feat considering the submicroscopic size of the tubes. To …