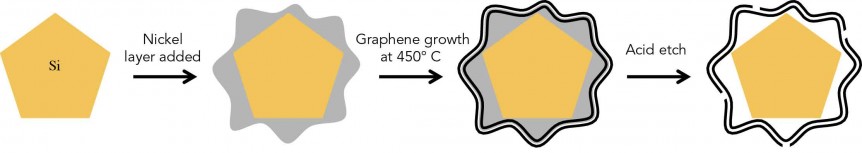
Dr. Yi Cui of Stanford University has expanded the idea of “battery” to include conductive ink on paper, fruit-like clusters of energy-storing capsules, and now, nano-sized graphene cages in which the energy can romp like a hamster in a plastic ball. He will be on hand at this year’s Sustainable Aviation Symposium on May 6, at the Sofitel San Francisco Bay hotel. His pioneering work with silicon as an electrode material goes back at least ten years, and has focused on overcoming silicon’s two major problems in battery use. Silicon expands and begins breaking down during repeated charge-discharge cycles. It reacts with battery electrolyte to form a coating that progressively destroys performance. The combination of crumbling and coating finally makes the battery inoperable. His group at Stanford had found a way to “wrap every silicon anode particle in a custom-fit cage made of graphene, a pure form of carbon that is the thinnest and strongest material known and a great conductor …
Tag Archive
Below you'll find a list of all posts that have been tagged as “the Battery Materials Research program of the DOE’s Vehicle Technologies Office”