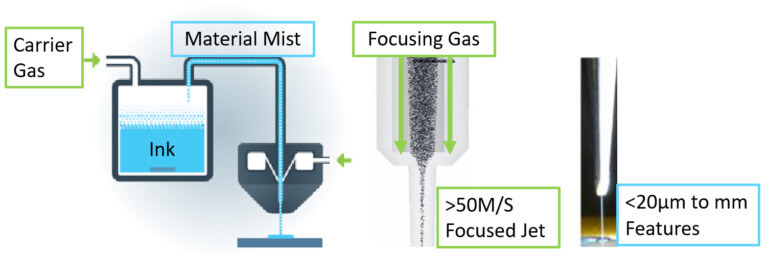
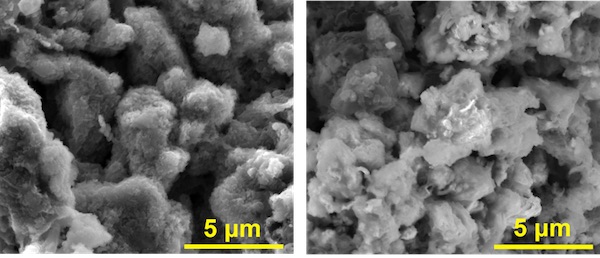
Dr. Jangwoo Kim has a resume’ that puts a great many qualifications together that spell “battery designer.” He has a B.S. degree in chemical engineering from Yonsei University, one of three “Sky Universities” regarded as South Korea’s most prestigious. At Cornell University, he received M. S. and Ph.D degrees in chemical engineering, and then worked for LG Chem on lithium-ion battery pack design. After that, he returned to Cornell to work on his Ph.D, investigating “next-generation rechargeable battery technology, including Li-Air and Li-Sulfur, specialized in inorganic nanomaterial synthesis and polymer processing via an electrospraying method.” He joined IBM Research, Almaden Research Center in 2016 and participated in the Battery 500 project, aiming to build a battery pack with a specific energy of 500 watt-hours per kilogram. We see the project leader, Dr. Winfred Wilcke, in a short video about that project. Battery 500 intended to reduce or eliminate heavy metals such as cobalt from the cells. Cobalt is not rare, but …
The C4V Battery – Solid-State in Production?
Jeffrey Engler of Wright Electric posted an item about Charge CCCV, LLC (C4V) which “demonstrated a prototype of its new Solid State Battery (SSB) at the NY BEST 2018 Fall Conference in New York. The Company’s SSB solution delivers higher performance, higher density, lower cost batteries that promise to require significantly less charging time than others.” The startup announced a 380 Watt-hour-per-kilogram battery already in production. Since your editor tends to become a bit snarky about the usual two-to-five-year period of anticipation before these numbers become reality, he rushed to check out the claims. Plausible Numbers, but Uncertain Time Frame The firm’s numbers are not wildly excessive, and they seem to be getting funding and finding partnerships with established companies. The video is not great proof of anything other than that a metal box with the company’s logo exists. Their web site gives credibility to their ability to produce actual batteries. According to C4V, “Approximately 80% of the cost to …
The 17X Aluminum-Air Battery?
Jaephil Cho has a surprise for us – an aluminum-air battery that is potentially (no pun intended) more energetic than gasoline. Director of the Research Center for Innovative Battery Technologies and Professor in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering, at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), Cho and his students have released over 350 papers, including one titled, “Seed-mediated atomic-scale reconstruction of silver manganate nanoplates for oxygen reduction towards high-energy aluminum-air flow batteries.” While such titles might not get him on the NY Times best-seller list, Cho is widely respected, UNIST reporting he has been named to the 2017 Highly Cited Researchers List in materials science, a second such honor for him. Professor Cho’ Surprise Professor Cho’s paper (in full) describes the aluminum flow battery he and his team developed. According to the UNIST News Center, “…Compared to the existing lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), the new battery outperforms the others in terms of higher energy density, lower cost, …
Promising 3D Printed Microlattice Battery
The three biggest words in battery structures are “Area, Area, Area.” The more anode and cathode area a battery can expose to the electrolyte that carries ions and electrons between the positive and negative ends of the battery, the better. Most battery configurations, according to researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and Missouri University of Science and Technology, block a great deal of interaction between these elements. Their solution is to go porous in a microlattice battery, thanks to 3D printing. Electrodes present some surface area to the electrolyte, which can only interact with the surface area presented. Rahul Panat at Carnegie Mellon and Jonghyun Park at Missouri S & T have created a cube-shaped battery composed of microlattice electrodes which present significantly greater amounts of surface area to the electrolyte. The title of their paper (with co-author Mohammad Sadeq Saleh) brings out this “area rule”: “3D printed hierarchically-porous microlattice electrode materials for exceptionally high specific capacity and areal capacity lithium …
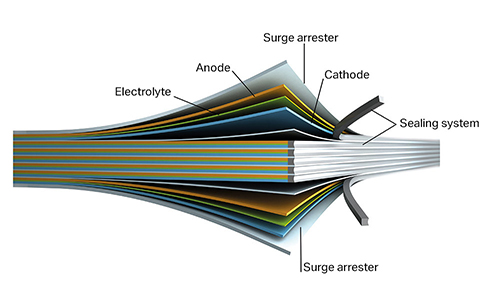
Oxis Energy Hits a Lithium-Sulfur Battery High
That near-mythical 10X (of current lithium cells’ energy density) battery hangs out there on the distant horizon, promising automobiles that can exceed 1,000 miles range, or light aircraft that can carry four at Cessna-like distances. Right now, we have two-place trainers good for an hour’s laps around the circuit, and the hope for improvements soon. OXIS Energy, a UK-based company, has achieved 425 Watt-hours per kilogram at the cell level, and looks to go higher in the near future. Lithium-Sulfur – A Worthy Alternative? Promoters of lithium-sulfur batteries suggest their products have several desirable characteristics and performance boosts that may transcend the limits of lithium-ion cells. Sion Power, for instance, claims availability of their Licerion battery with an even better 500 Watt-hours per kilogram and 1,000 Watt-hours per liter. On the same track, OXIS Energy has announced they have a demonstrated 425 Wh/kg cell, expected to rise to 450 Wh/kg by the end of the year and to 500 by …
John Goodenough’s Counterintuitive Battery
A Long and Productive Life On his 96th birthday today, John Goodenough and his research team’s latest findings are the subject of much speculation. He, fellow scientist Maria Braga, and his research team have created a battery claimed to be three times as energy dense as existing lithium-ion contemporaries, but exhibiting the counterintuitive property of improving with repeated charging cycles. Goodenough’s career began in 1943 (a year after your editor was born) with the award of his bachelor’s degree in mathematics from Yale University, followed his master’s and Ph.D. in physics from the University of Chicago in 1951 and 1952 respectively. He worked at MIT and in 1976, left to become head of Oxford University’s Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory from 1976 to 1986. In 1986, he assumed the Virginia H. Cockrell Centennial Chair in Engineering at the University of Texas at Austin, at an age where most men are cashing in their 401k’s. Texas Monthly comments on the counterintuitive nature of …
Battery Options for Range and Longevity
Two varying approaches to battery development may hold clues to future directions for energy storage. At the same time, their announcements, promising as they seem, reinforce our cautious attitudes toward how battery performance numbers are presented. PNNL Attacks the Electrolyte Issue According to Green Optimistic, “Researchers from the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) have developed a new formula for battery’s electrolyte solution to enhance its performance unprecedentedly in terms of its service life and storage capacity or an electric vehicle’s range.” The video gives an overview of what it takes to make a battery and hints at the reasons battery research takes so long to give up improved energy storage devices. Unprecedented the development may be, and the promise of a battery with a 7X longer lifespan and two-to-three times longer range than currently-available batteries certainly captures our attention. Its own press release suggests that PNNL researchers are enthusiastic about the longevity of their new chemistry. “When it comes to …
Better Battery Materials – Asphalt?
Asphalt, Graphene, and a Lithium Coating Mike Williams, reporting for Rice University in Houston, Texas, writes, “A touch of asphalt may be the secret to high-capacity lithium metal batteries that charge 10 to 20 times faster than commercial lithium-ion batteries, according to Rice University scientists.” We’ve written about James Tour and his laboratory before. He and his students come up with a plethora of new energy ideas and are able to demonstrate some exciting outcomes. His latest effort mixes asphalt with conductive graphene nanoribbons, and then electrochemically coats the composite with lithium metal to form a battery anode. The anode, when combined with a sulfurized-carbon cathode, was used in full batteries for testing. The results seem a bit incredible, with the ability to charge 20 times faster than commercial lithium-ion batteries. Being able to “refill” your electric car or airplane in five minutes rather than two hours or more would make electric vehicles practical alternatives to their fossil-fuel-powered cousins. After …
EMBATT – an Embedded Battery that combines Structure and Energy
Imagine a battery that reduces the overall number of structural parts in an electrical vehicle and the volume taken up by the battery. That’s the concept behind EMBATT (chassis embedded battery), which functions as structural energy storage. It can cut the volume occupied by a battery in half, with serendipitous outcomes for lightness and structural efficiency. This is similar to NASA-backed research on cubesat walls that also function as energy storage structures. IAV is a German firm that provides consultation and partnerships with leading automotive companies. It specializes in synergistic concepts and system-level thinking. The company, working with Fraunhofer Institute for Ceramic Technologies and Systems IKTS in Dresden, and Thyssen Krupp System Engineering ,“Want[s] to use our experience from automotive development for renewable energies and decentralized energy supply.” It sees strong links between these endeavors, and works to combine technologies that will enable greater efficiency. Think of a Tesla battery pack, composed of individual cells connected in series and parallel …
Silicon, Sulfur and 3D graphene Makes High-Performance Battery
Lithium-sulfur batteries display winning qualities, such as low production cost, environmental friendliness, and high energy density. Researchers usually give up, or look elsewhere, when the materials’ poor cycle life and loss of active materials on both anode and cathode show up. Researchers at Beihang University in Beijing report developing “a new Li-sulfur battery using honeycomb-like sulfur copolymer uniformly distributed onto 3D graphene (3D cpS-G) networks for a cathode material and a 3D lithiated Si-G network as anode.” They report “a high reversible capacity of 620 milli-Amp hours per gram, [and an] ultrahigh energy density of 1,147 Watt-hours per kilogram (based on the total mass of cathode and anode), good high-rate capability and excellent cycle performance over 500 cycles (0.028% capacity loss per cycle).” The materials used in the cathode and anode presented challenges. The “inherent insulation of sulfur” on the cathode and the high solubility of polysulfide intermediates cause an inability of the active materials to respond to one another, …